

Thus, in Stop & Wait ARQ technique, the minimum number of sequence numbers required is equal to the sum of sender window size & receiver window size

Stop & Wait ARQ is a 1-bit sliding window protocol where the size of the sender window as well as the receiver window is 1.

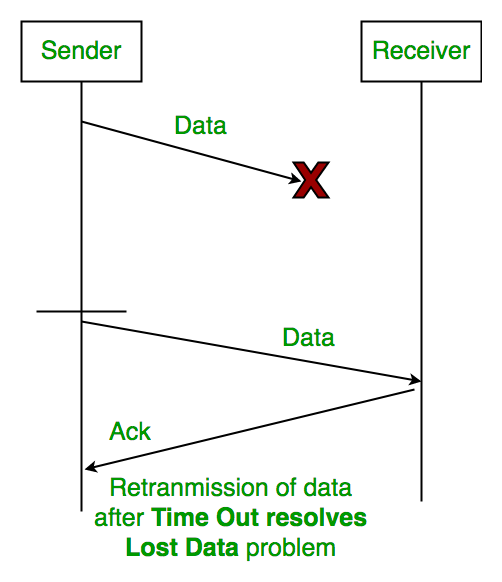
Note: If any sliding window protocol must work properly then, the available sequence numbers must be greater than or equal to the sum of sender window size and receiver window size. Working of Stop & Wait ARQ is almost like Stop & Wait protocol, the only difference is that it includes some additional components, which are: Stop & Wait ARQ also assumes that errors may occur in the data while transmission. Stop & Wait ARQ assumes that the communication channel is noisy (previously Stop & Wait assumed that the communication channel is not noisy). Stop & Wait ARQ is a sliding window protocol for flow control and it overcomes the limitations of Stop & Wait, we can say that it is the improved or modified version of Stop & Wait protocol. Stop & Wait Protocol performs better for LANs than WANs because the efficiency of the protocol is inversely proportional to the distance between the sender & receiver node and as we all know that the distance is less in LANs as compared to WANs.īut this protocol has some issues, one such issue is the probability of occurrence of deadlock, which is very high due to loss in a data packet or loss in feedback which can lead to infinite waiting, where the sender will keep on sending the data packet if the feedback is lost. Then, the receiver node sends the feedback to the sender node (about the received data packet).Īfter receiving the feedback, if the feedback is positive then the sender node sends the next data packet otherwise resends the damaged packet. Then, waits for the feedback of the transmitted packet.Īs soon as the receiver node receives a data packet it starts processing it. The sender node sends a data packet to the receiver node. The stop & wait protocol is half-duplex whereas sliding window protocol is full-duplex. And, in stop & wait protocol sorting is not necessary, but in sliding window protocol, sorting may be or may not be necessary. Talking about the efficiency, the efficiency of stop &wait protocol is less, while the efficiency of the sliding window protocol is more than stop & wait protocol. On the other hand, in the sliding window protocol, the sender node keeps on sending frames to the receiver node without waiting for any feedback and it re-sends the frame which is/are damaged or suspected. The basic difference between them is that, in stop & wait the sender node sends one frame and then waits for the feedback from the receiver node. In the above diagram, we can see that there are two protocols, Stop & Wait and a sliding window. Flow control in computer networks is defined as the process of managing the rate of data transmission between two systems(nodes), this mechanism ensures that the rate of data (transmitted by the sender) is within the receiving capacity of the receiver node.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
